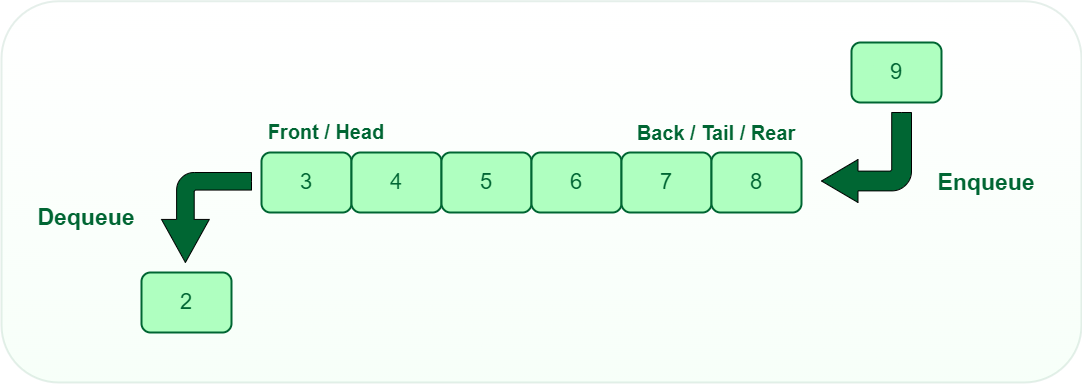
In C, a queue can be implemented using an array or a linked list. Here’s an example of how to implement and use a queue with an array. This example includes functions to enqueue (add an item to the queue), dequeue (remove an item from the queue), and check if the queue is empty or full.
### Queue Implementation in C using Arrays
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define SIZE 5 // Define the maximum size of the queue
struct Queue {
int items[SIZE];
int front, rear;
};
// Initialize the queue
void initialize(struct Queue *q) {
q->front = -1;
q->rear = -1;
}
// Check if the queue is full
int isFull(struct Queue *q) {
return (q->rear == SIZE - 1);
}
// Check if the queue is empty
int isEmpty(struct Queue *q) {
return (q->front == -1 || q->front > q->rear);
}
// Enqueue an element into the queue
void enqueue(struct Queue *q, int value) {
if (isFull(q)) {
printf("Queue is full! Cannot add %d\n", value);
} else {
if (q->front == -1) {
q->front = 0;
}
q->rear++;
q->items[q->rear] = value;
printf("Enqueued %d\n", value);
}
}
// Dequeue an element from the queue
int dequeue(struct Queue *q) {
int item;
if (isEmpty(q)) {
printf("Queue is empty! Cannot dequeue\n");
return -1;
} else {
item = q->items[q->front];
q->front++;
if (q->front > q->rear) { // Reset the queue if empty
q->front = q->rear = -1;
}
printf("Dequeued %d\n", item);
return item;
}
}
// Display the elements in the queue
void display(struct Queue *q) {
if (isEmpty(q)) {
printf("Queue is empty!\n");
} else {
printf("Queue elements: ");
for (int i = q->front; i <= q->rear; i++) {
printf("%d ", q->items[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
// Main function to test the queue
int main() {
struct Queue q;
initialize(&q);
enqueue(&q, 10);
enqueue(&q, 20);
enqueue(&q, 30);
enqueue(&q, 40);
enqueue(&q, 50);
display(&q);
dequeue(&q);
display(&q);
enqueue(&q, 60); // This will show that the queue is full
return 0;
}
### Explanation
1. Queue Structure: We define a Queue struct that includes an array items of a fixed size, and two integer variables front and rear to keep track of the front and rear of the queue.
2. Initialization: The initialize function sets both front and rear to -1, indicating an empty queue.
3. Enqueue: The enqueue function checks if the queue is full. If not, it adds the element at the rear and increments the rear index.
4. Dequeue: The dequeue function removes an element from the front, increments the front index, and resets both front and rear if the queue becomes empty.
5. Display: The display function iterates from front to rear and prints the elements in the queue.
This array-based queue has a fixed size. If you need a dynamic size, consider implementing the queue using a linked list instead.