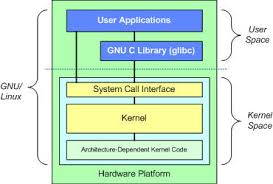
The Linux kernel is the core component of the Linux operating system, managing hardware resources and providing essential services to applications. Modifying the kernel can be a daunting task, but with the right approach, it can be a rewarding experience. This guide will walk you through the basics of making changes to the Linux kernel.
1. Setting Up Your Environment
Before you start, ensure you have a suitable development environment. You’ll need:
A Linux distribution (e.g., Ubuntu, Fedora)
Essential development tools (e.g.,
gcc,make,git)Sufficient disk space and memory
Install the necessary packages:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install build-essential libncurses-dev bison flex libssl-dev libelf-dev
2. Downloading the Kernel Source
Download the latest kernel source code from kernel.org:
wget https://cdn.kernel.org/pub/linux/kernel/v6.x/linux-6.6.tar.xz
tar -xvf linux-6.6.tar.xz
cd linux-6.6
3. Configuring the Kernel
Configure the kernel options using one of the configuration tools:
make menuconfig
This command opens a text-based interface where you can enable or disable kernel features.
4. Making Changes
Navigate to the part of the kernel source code you want to modify. For example, to change a driver, go to the drivers directory:
cd drivers
Make your changes using a text editor like vim or nano.
5. Building the Kernel
After making your changes, build the kernel:
make -j$(nproc)
This command compiles the kernel using all available CPU cores.
6. Installing the Kernel
Install the newly built kernel:
sudo make modules_install
sudo make install
Update your bootloader configuration (e.g., GRUB) to include the new kernel:
sudo update-grub
7. Rebooting
Reboot your system to use the new kernel:
sudo reboot
8. Testing and Debugging
After rebooting, verify that your changes are working as expected. Use tools like dmesg to check for kernel messages and debug any issues.
Conclusion
Modifying the Linux kernel can be complex, but it’s a valuable skill for anyone interested in systems programming or operating systems. By following these steps, you can start making your own changes to the kernel and contribute to the open-source community.
Happy hacking!
Feel free to ask if you have any questions or need further details!